Sleep is essential for life. I think the most important factors for a healthy body are eating (healthy whole food), sleeping and exercise. Poor sleep quality and duration are associated with decreased immune function, increased stress hormones (that suppress the immune system), mood disorders, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
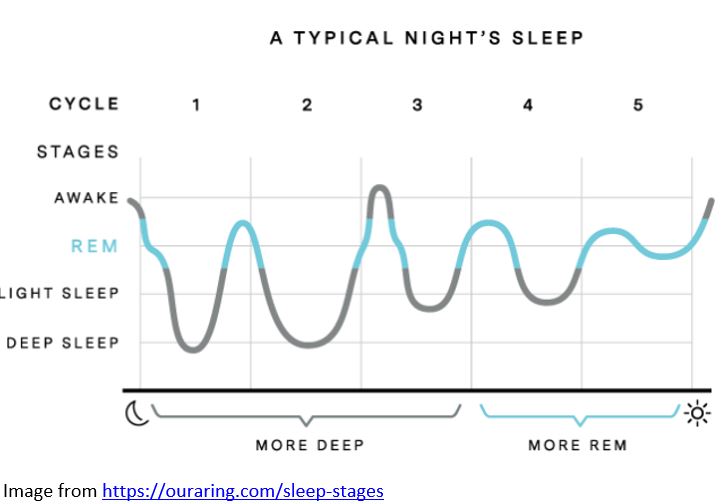
In a normal night, we go through about 4-6 cycles of sleep and each stage contains varying amounts of light sleep, deep, sleep and REM sleep. Deep sleep is important for regeneration of the body, including the immune system, and REM sleep is important for regeneration of the brain.
Stages of sleep
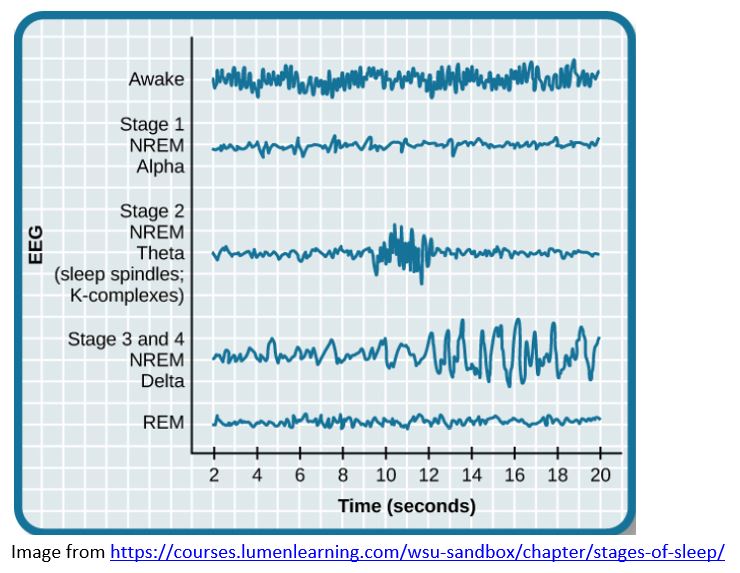
Awake – stage 0
Light sleep – stage 1 and 2
- We typically spend around 45-55% of the night in light sleep
- EEG shows non-REM alpha and theta brain waves
- Blood pressure, body temperature, breathing, and heart rate start to decrease
- Muscles relax and you may jerk awake
- You can be woken up easily during this stage
Deep sleep – stage 3
- We typically spend 15-25% of the night in deep sleep, mostly within the first 4 hours
- EEG shows long, slow delta brain waves
- Deep sleep is the most important for body recovery
- Blood pressure, blood flow decreases, body temperature, breathing, and heart rate further decrease
- Muscles very relaxed and have increased blood flow – especially important for recovery from exercise
- Brain increases cerebral spinal fluid that flushes the brain of metabolic waste
- Hormones involved in growth and repair are produced – deep sleep is the most restorative and rejuvenating stage
- Difficult to wake from this stage, if an alarm or person wakes you at this stage, you can feel groggy and temporarily disoriented
- This stage will increase after periods of sleep deprivation or intense exercise
REM sleep – stage 4
- We typically spend 20-25% of the night in REM sleep, which is when we dream, primarily in the last 4 hours
- EEG show low amplitude mixed brain waves that look similar to when awake
- REM sleep is the most important for brain recovery
- Brain activity is high
- Muscles are inhibited so that you don’t act out your dream – everyone dreams even if you don’t remember them
- This stage of sleep is important for consolidation of memory, learned information, and problem-solving
How does sleep influence the immune response?
Cytotoxic T cells are the key immune cells that kill virus infected cells. The adaptive immune response is highly supported by regenerative hormones produced during the deep sleep stage, such as growth hormone. Sleep deprivation significantly inhibits the immune response. A lack of sleep is high stress for the body causing cortisol to be released, cortisol inhibits the immune system. This is why even just one night of poor sleep can dramatically increase your risk of getting a cold or flu. Also, when we have an infection, our need for sleep increases, which is why being sick can make us feel so lethargic. If you are sick and tired of being sick and tired then listen to your body and get more sleep 🙂
Sleep deprivation causes an increase in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and IL-6 that promote chronic inflammation. Lack of sleep also reduces the number of helper T cells and Natural Killer cells. Helper T cells are important for activating the proliferation of the cytotoxic T cells that kill virus-infected cells. Natural Killer cells also kill virus-infected cells.
According to the National Sleep Foundation, sleeping more won’t necessarily prevent you from getting sick, but it can significantly decrease the severity of infection. We need enough sleep to effectively produce cytokines required to effectively stimulate the immune cells to fight infections. If you do get sick, have lots of naps! We make more cytokines and immune cells during sleep. Plus, the immune system uses a lot of energy to fight infections; sleeping helps your body allocate ATP to the immune system.
Getting enough sleep also helps to protect you from chronic inflammatory diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. Obesity is also affected by chronic inflammation, so increasing sleep can help to reduce abdominal fat that is highly correlated with cardiovascular disease. It has been shown that napping helps to reduce cortisol…..which will reduce belly fat and chronic inflammation, and increase immune function.
Factors that inhibit sleep:
- Chronic stress – epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine are stimulating neurotransmitters made during stress along with cortisol. Stimulating neurotransmitters can keep you up at night ruminating and problem-solving. Our brain has evolved to be great at problem-solving and sometimes it decides that night time is the best time to try and resolve all issues.
- Drinking excess alcohol – as alcohol is broken down it produces stimulating molecules that disrupt sleep. Alcohol may make you feel more like sleeping initially but during the course of the night it reduces deep sleep and reduces REM sleep.
- Over-consumption of stimulants – caffeine can stay in the body for up to 6 hours.
Factors that promote sleep:
- Get an hour of moderate exercise during the day, more than 3 hours before you want to sleep. Deep sleep is required for restoring and regenerating cells. Exercise stimulates the production of growth hormone that is the primary hormone made at night, specifically during deep sleep. Exercise stimulates an increase in the amount of deep sleep you have at night.
- Try and have a daily routine, even when you aren’t working. Go to bed at the same time and wake up at the same time (give or take an hour on the weekend). We make growth hormone during deep sleep, more cortisol in the morning, and more melatonin in the evening. Having a sleep schedule helps these hormones to become very optimal and regulated.
- If you have trouble falling asleep, have a small snack an hour before you want to sleep. Something with protein and a bit of carbs, like peanut butter on toast or a couple crackers with cheese, a handful of nuts and a tea with honey, ½ cup yogurt with some berries. When we eat carbohydrates we produce serotonin….serotonin is the precursor for melatonin and we need melatonin to sleep. Having the protein with the carbs helps to keep your blood sugar stable. If you have too much sugar before bed, you will make insulin and then your blood sugar will drop while you sleep….a drop in blood sugar causes the production of epinephrine that will wake you up.
- Get natural light during the day. Natural light stimulates your brain to be awake and alert and then in the evening when light decreases, your brain is more likely to make melatonin. Studies have shown that as little as 2 hours of natural light during the day is enough to increase sleep quality by 80%.
- Reduce blue light during the evening. Blue light stimulates your pineal gland and prevents melatonin production. Use your blue light filter on your phone in the evening and reduce flashing lights like video games and TV.
- Distract your brain if ruminating. If you find your brain trying to solve all of life’s problems when you are trying to fall asleep, the only way to stop this cycle is to distract it. If you have other ideas for this one then leave a comment in the comment section but I find that the best thing is to read a book. It might also help to write a to-do list so you won’t worry about forgetting to do something.
- Some herbs that increase relaxation. Some of these can be found in combination in teas like “bedtime tea” or “sleepytime tea” – valerian root, theanine, lavender, chamomile, kava kava, rhodiola, ashwagandha, and passionflower.
Fun Fact: Prolonged sleep deprivation of 3-4 days will cause severe cognitive impairments, delusions, psychosis and paranoia. People that have Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI) and have total sleep deprivation will die within approximately 6 months. FFI is a rare genetic disease where the brain gradually deteriorates and ultimately results in coma and death.


Great info! I love the comment about getting two hours of natural light and how it affects sleep. I try to do “no screens after 9:00p.m.” and it really helps my sleep. Thanks Wendi!