Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that has several important functions in our body. Getting into the winter months, it may be time to think about adding a vitamin D supplement. Studies show that approximately 40-50% of North Americans and about 1 billion people worldwide are deficient in vitamin D.
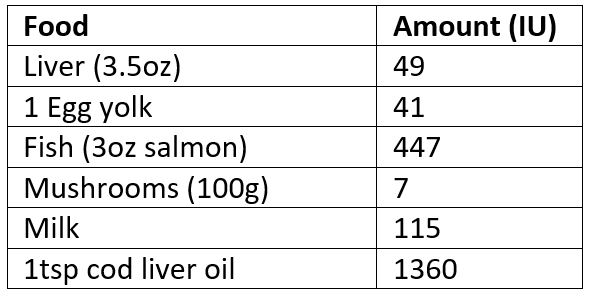
Vitamin D is primarily made in the stratum basale layer of our skin when we are exposed to UVB sunlight (below I made a diagram of the steps involved in its production). We can get some from consuming liver, eggs, oily fish, mushrooms, and fortified milk but food is only a minor source compared to sun exposure or supplementation. Fat-soluble vitamins can be stored in our liver so there is a supply to draw on for a period of time. If you had about 10-20 minutes of sun exposure a few days per week during the summer, you likely have enough vitamin D in your liver to last until around Christmas time. So then we might want to consider supplementing with a little extra to ensure that we have optimal levels to get us through to spring.
Vitamin D has many essential functions:
- Essential for calcium regulation between the bones and the bloodstream. Vitamin D signals the small intestine to produce transporters that take up calcium from the diet. If you are deficient in Vit D then you cannot absorb calcium from food. Vitamin D deficiency causes bone malformation, called rickets in children and defective bone mineralization, called osteomalacia in adults. This is why cod liver oil became a common supplement in the early 1900s; cod liver oil contains vitamin D and prevented rickets.
- Required for regulation of phosphate metabolism
- Regulates immune function and has been associated with a decreased risk of cancers, for example, optimal Vit D levels reduce the risk of colorectal cancer by 50%
- Regulates immune function so that we are better able to fight off infections like the flu
- Regulates immune function to inhibit excess stimulation, so vitamin D is very beneficial for people with autoimmune diseases, especially multiple sclerosis and lupus
- Vitamin D supplementation has been shown to reduce the severity of depression comparable to antidepressant medication – this is significant when winter depression (Seasonal affective disorder) is estimated to affect 10% of the population
- Reduces risk of cardiovascular disease
- Regulates glucose metabolism and helps prevent glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes
How is Vitamin D made?
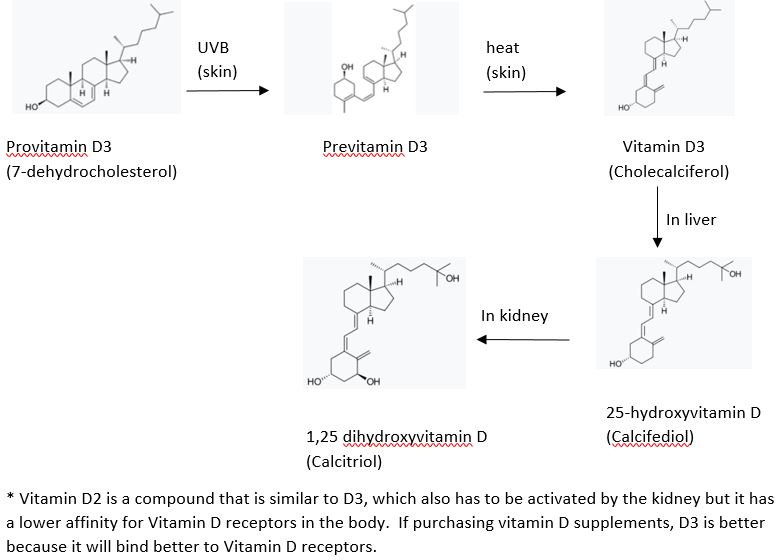
In our skin, cholesterol is converted into Provitamin D3, then UVB sunlight converts that into previtamin D3 and then the heat from the sun on our skin converts that into vitamin D3. This is then transported through the bloodstream to the liver and it converted into 25-hydroxyvitamin D (this is the main circulating form that is detected in a blood test measuring serum vitamin D levels). The last step is the conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D into 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D in the kidneys when stimulated by parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called calcitriol, and this is the active form that binds to vitamin D receptors in almost every cell of the body.
How much vitamin D do we need?
- If you get a blood test to look at blood levels of Vitamin D (25-hydroxyvitamin D), you want your levels to be above 50nmol/L (nanomoles per litre). Serum levels of 50-150nmol/L is considered optimal. Guidelines recommend that blood levels below 30nmol/L should be treated with a supplement. It is not clear how much vitamin D is too much but it seems that blood levels would have to be extremely high, such as 375nmol/L is required to cause hypercalcemia (high blood calcium levels).
- How much sun = Vit D supplement? As an example, someone with medium-fair white skin, at noon in Miami Florida, in the summer, with face, arms, and legs exposed will produce about 1000IU of Vitamin D in about 6 minutes. Multiply the time by 2-6X for darker skin. Keep in mind that this is a very approximate number just to give you a general idea. Also note that latitude, altitude, time of day, season, skin pigmentation, and age affect how much vitamin D is produced in the skin. It is not possible to make vitamin D at all in regions that have winter. Also note that sunscreen blocks UVB rays and therefore inhibits the production of vitamin D. It has been documented that people living in warm sunny locations can still be vitamin D deficient.
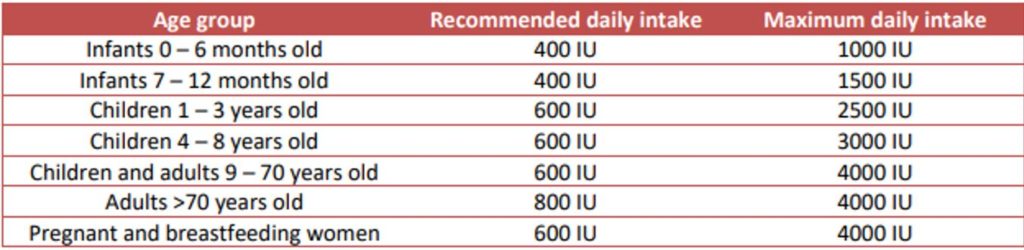
- The Canadian daily recommended amount is 400-800IU per day but this is quite low; it would be enough to prevent rickets but is not an optimal amount. The upper limit suggested in Canada and the US is 4000IU/per day but 1000-2000IU per day is usually enough to reach optimal levels for most people.
Food Sources
What about Tanning beds?
Tanning beds produce both UVA and UVB rays that have the wavelength required for the production of vitamin D and they may be a beneficial way to make Vitamin D because the entire skin surface can be exposed for a very short period of time to produce a significant amount of vitamin D. Having very short exposure times means that the risk of skin cancer is quite low but excessive exposure can cause skin cancer. Health Canada provides exposure time regulations for artificial tanning clinics to prevent people from exceeding time limits. 10-15 minutes in a tanning bed only once per week can produce 10,000 IU of vitamin D.
References
Vitamin D testing and treatment – a review of current evidence
Meta-Analyses of Vitamin D intake and colorectal cancer risk
Preventative effect of Vitamin D on seasonal influenza
Vitamin D and MS – MS Society of Canada
High serum vitamin D may protect against multiple sclerosis
Summary of research articles evaluating impact of Vitamin D
Vitamin D and depression – A systematic review
How much sun is equivalent to Vitamin D supplementation
Sunbeds can produce physiological levels of vitamin D


I am currently in the Philippines with about 30 degree weather every day. It’s amazing to take in the sun for about 20 minutes of my day, but I have noticed I get a white dot pigmentation often times during the summer? Have any ideas what that could be?
Thanks Wendi!
Wow, great weather! White dots can happen when your melanocytes (the cells in your skin that make the brown pigment when you tan) stop making melanin. It shouldn’t be a concern but if it increases then talk to a doctor to see if anything else might be going on 🙂