GABA stands for Gamma Amino butyric acid. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that decreases the stimulatory effects of excitatory neurotransmitters. Without inhibition, our brain would be constantly over-stimulated and that would feel like anxiety and to some extremes, panic. GABA is the most calming neurotransmitter we have. Glutamate is one of the primary stimulating neurotransmitters in our brain that helps us to think, problem-solve, learn, and remember. It is ideal to have a balance between GABA and glutamate so that we can think and problem-solve but also remain calm.
How are GABA and glutamate produced?
Glutamate is made from an amino acid called glutamine. Glutamine is found in many plant and animal foods and should be easily acquired in a healthy diet. Glutamate production is increased when we have stress so that we can think and problem-solve, and under normal conditions, an increase in glutamate should stimulate an increase in GABA so that we can feel alert but also calm. If glutamate levels increase and GABA does not, then you will feel anxious, overstimulated, less able to focus your attention, and perhaps have difficulties sleeping. It is dose-dependent so the less GABA you have then the stronger the symptoms will be. In the diagram below, glutamine will form glutamate during stress and glutamate will convert into glutamine when stress decreases. Glutamate increases should be accompanied by GABA increases but that is not always the case.
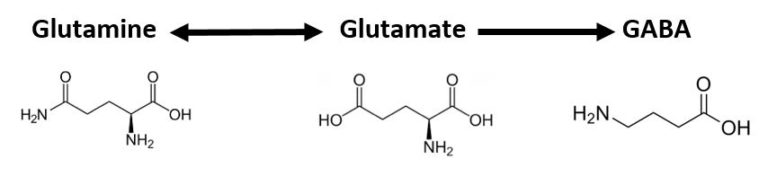
Excessive glutamate that is not countered by GABA can cause excitotoxicity that can cause neuron cell death. Glutamate causes calcium to enter the neurons; in excess this damages mitochondria (organelles that make energy), increases free radical formation causing oxidative damage, and increases apoptosis (programmed cell death). Alcohol withdrawal can have a significant effect on glutamate levels in the brain. Drinking alcohol initially inhibits the production of glutamate, which is why alcohol can have a calming effect, however, once alcohol is out of the system there is a rebound effect that causes an increase in glutamate the next day. The day after drinking alcohol some people can feel more anxiety than normal…the more alcohol consumed, the stronger this effect. This is why it can sometimes be very dangerous for alcoholics that have severe withdrawal symptoms.
Fun Fact: Blood sugar is important for removing glutamate from the synaptic cleft so if you happen to find yourself in a hangover situation, sipping orange juice or something sweet would help.
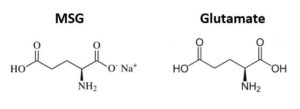
MSG is monosodium glutamate
MSG is a common flavour-enhancing molecule that tricks our brain into thinking processed foods taste delicious, and it can bind to glutamate receptors and can increase the effects of our brain’s natural glutamate. If you are dealing with anxiety then it would be a really good idea to avoid excess MSG.
MSG is naturally produced in some foods such as old cheeses, and tomatoes. The main issue with foods containing added MSG is the dose.
When reading the ingredients on food packages the following ingredients are MSG:
- Seasoning
- Hydrolyzed vegetable protein
- Textured vegetable protein
- Yeast extract
- Soy extract
- Soy protein isolate
- Autolyzed yeast extract
- Sodium caseinate
- Calcium caseinate
Beware of GABA-mimicking drugs
Benzodiazepines are medications that mimic the effects of GABA; these include drugs such as valium, Xanax, Ativan (lorazepam), diazepam, any-kind-of-azepam. These medications are used to treat severe anxiety but they are highly addictive in the sense that your brain stops producing its own GABA and then stopping these kinds of medications can cause a dramatic increase in glutamate and therefore, more anxiety. I would caution you to be very careful of getting into any kind of benzodiazepine habit if you have chronic anxiety or panic attacks. It is the type of medication you take only once in a while when very necessary, but not on a regular basis. If medication is required, most doctors prescribe one of the anti-depressant medications that most commonly affect serotonin and they may or may not be effective.
How can we make our brain produce more GABA?
Two main requirements for the brain to produce GABA is the availability of glutamine and vitamin B6. Vitamin B6 is essential for the conversion of glutamate into GABA. B6 is found in meat, eggs, many vegetables, and whole grains. Glutamine is found in many foods and can also be taken as a supplement. Glutamine has other benefits including helping muscles to recover from exercise and helping to heal the intestinal lining. Taking glutamine as a supplement does not mean your brain will use it to make GABA but some people find it helps.
There is not a lot of research that supports the effectiveness of taking GABA itself as a supplement. One main issue is that GABA does not easily cross the blood-brain barrier, it needs to be made in the brain. Some people do notice a benefit from GABA supplements, unfortunately it may indicate that there is generalized inflammation occurring in the body, which would cause little gaps in the blood-brain barrier and that would allow the GABA to enter. Inflammation can cause an increase in glutamate so helping your body to reduce inflammation is an important way to reduce excess glutamate production….but then the GABA supplement won’t work. A little bit of a catch 22 but if you reduce inflammation then you may not need the extra GABA. Even though GABA cannot technically cross the blood-brain barrier as far as we know, many people do experience calming effects from taking it as a supplement so if it works then awesome. It is possible that we just don’t know how it works at this point. Most studies are done on animals because it is not very ethical to use humans and take brain biopsies, ha. Even if it is a placebo effect, if it helps then great! Side effects are rarely reported but some people have found it may cause upset stomach, headaches, or feeling overly tired.
One supplement that has been shown to increases the production of GABA is theanine, also found in tea. See theanine article here.
Gut Bacteria make GABA!
Another important factor is the role of gut bacteria. It has been found that certain strains of probiotic organisms, specifically lactobacillus and bifidobacterium were effective at increasing GABA production in the enteric nervous system – the nervous system in our digestive tract. There is a lot of research showing a major connection between the health of the digestive system and the health of the brain. There is considerable communication between the digestive tract and the brain through the vagal nerve. Vagal nerve stimulation has been shown to increase the level of GABA in cerebral spinal fluid. It may be that concentrating on a healthy digestive tract can help reduce anxiety. A probiotic supplement may be more beneficial than a GABA supplement!
It has also been shown that gut bacteria can control tryptophan metabolism by converting it into 5-HTP, which is then converted into serotonin, our anti-depression neurotransmitter.
Fun Fact: There are about 200-600 millions neurons in the enteric nervous system and about 86 billion in our brain.


Nasty! Camouflaging MSG by calling it something else! I had no idea it was high in old cheese — maybe that’s why I enjoy extra old cheese so much, AND why I always have trouble sleeping after eating cheese! Thanks Wendi — always informative!!
This is very interesting. As I am prone to anxiety, understanding these transmitters helps and now I am trying to use my diet as a weapon against anxiety. I wonder, if you had to create a shake that could cure anxiety, what foods would you incorporate?
That is a great question. My first thought is that I would make bone broth, simmer bones, cartilage and skin with salt, onion, garlic, and some parsley for 20-24 hours. The cartilage, bones, and connective tissue contains a high amount of the amino acid glycine, that also acts like GABA and causes the nervous system to relax. The second part of reducing anxiety involves decreasing inflammation, they are highly connected, so things like turmeric, omega 3 fatty acids and antioxidants. The last thing I would think of is probiotics because of the gut-brain connection is all about how the bacteria in our gut regulate immune function as well as make short chain fatty acids that is good for our brain. So a shake of some kind should include yogurt, turmeric, fresh juiced veggies and some fruit for taste, can also include cinnamon and magnesium – that is a mineral that is very important for calming the nervous system 🙂
Wendi